Innovative sustainable built environment laboratory
- KEYWORDS
- sustainability
- built environment
- Innovation
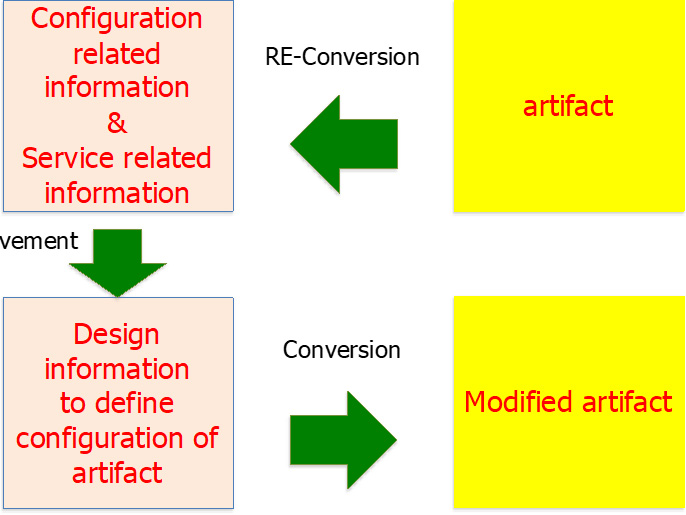
Digital twin for sustainable built environment
How could we facilitate innovation that could enhance sustainable built environment?
Japan has a building stock of over 9 billion square meters, while the annual new build is less than 0.15 billion. The fact indicates that we must make existing buildings sustainable, though they could deteriorate and become outdated if we give up proactive maintenance and management. Such actions require information on “How a building is composed and how the building is operated”. However, that information is not always available. The research aims to establish the digital twin method, as shown in the left figure, where information on artifacts is extracted to establish a configuration and service-related information model. This model is the basis for designing re-configuration and re-sevitization. Then, the information model is converted to the modified artifact in the real world.
The idea of “information embedded building”
INFORMATION EMBEDDED BUILDING’ FOR SUSTAINABLE LIVING: Tomonari YASHIRO・Proceedings of the 2008 World Sustainable Building Conference,2008.12
Research staff
Project Professor
Tomonari Yashiro
Sustainable building, Innovation Management

Origination of the research
In 1994, the Musashi Institute of Technology (Tokyo City University) team published a conference paper that quantified buildings' embodied energy/carbon. This paper is a very early example of evidence-based research on sustainable building. Since then, Yashiro and his colleagues have pioneered research relating to sustainable built environment.
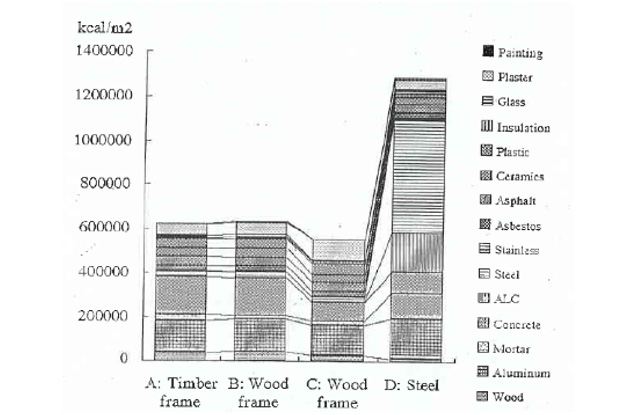
Embodied Energy quantification as for different structured detached houses in Japan
Tomonari Yashiro、 Nobuhiro Yamahata、 ’Energy use and CO2 emission by constructing houses’、 Proceedings of CIB TG8 symposium、 Building Research Establishment、 1994.5
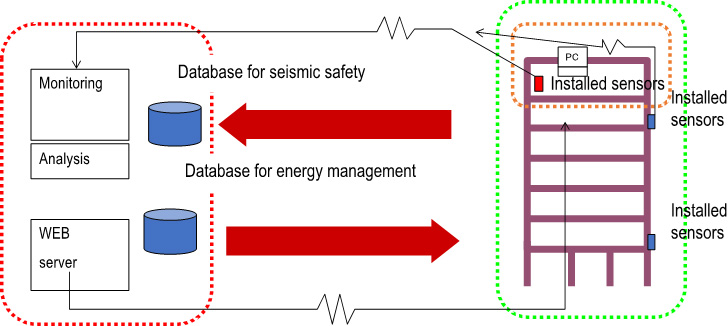
Current research
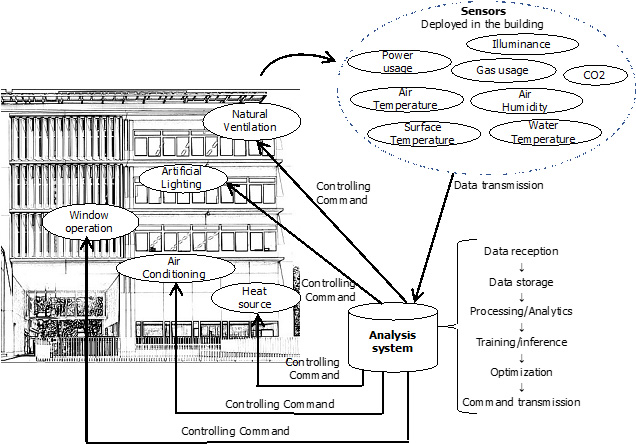
Holistic indoor and energy management system using IoT
The system integrates and optimizes the operation of air conditioning, ventilation, lighting and windows by collecting and analyzing the data from various sensors deployed in the building. The laboratory has developed and innovated the system since 2005. The figure is an example of the system installed in the Komcee21 building on Komaba campus of the University of Tokyo. Associated Professor Hiroyuki Shida has led the technology development of integrated control of windows, air conditioning and lighting.

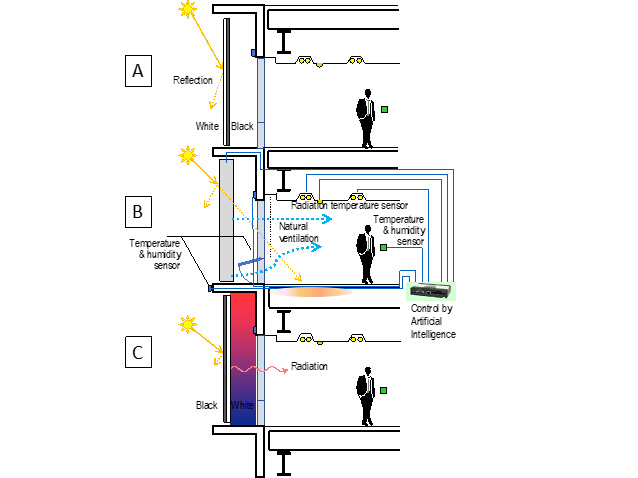
Introduction of carbon trading to facilitate operational energy reduction
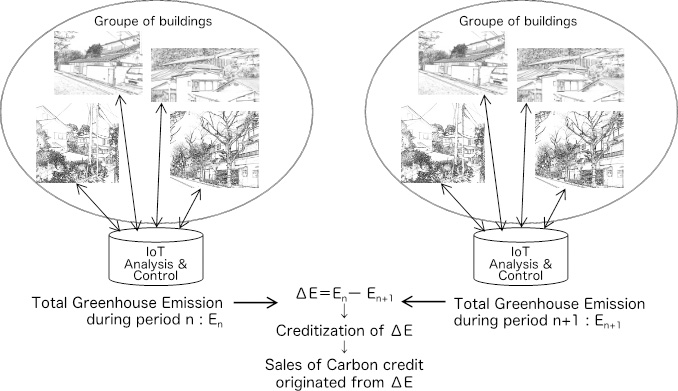
IoT enables the measure, reporting and verification of the quantity of energy use and green gas emission from the operation of buildings by reasonably small transaction cost. The laboratory persuades the way the enabler could contribute to the diffusion of carbon trading in the built environment.
Possible aggregator of carbon credits from a set of operational energy use reductions using IoT
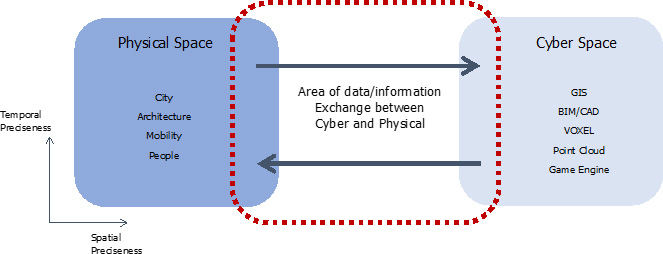
Conceptualization and realization of Interspace as a core of digital-twining for the built environment
(Collaborative research with Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo)
For a sustainable built environment, it is essential to provide common ground of spatial models that are universally usable by various sectors of different domains. The laboratory is preparing an experimental version of the common ground spatial model of Tokyo City University campus. The model is expected to be usable in various ways by students and researchers of the university.
Publications for diffusion of knowledge that could facilitate innovation.


