Research center for Management of Infrastructure and Natural Disaster control
KEYWORDS
- Management of Infrastructure construction and maintenance
- Natural Disaster control
- Information sharing of the scientific knowledge from academic research to civilian population
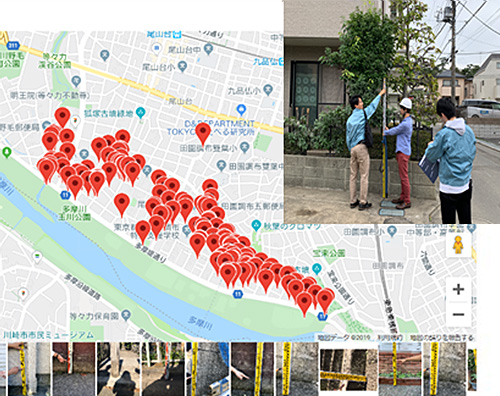
Inundation damage survey in Tamazutsumi /
Denenchofu area of Tokyo due to the Typhoon Hagibis (Typhoon No. 19)
- ● Smart management of infrastructure construction and maintenance
- ● To minimize impact of the intensifying natural disasters on the social infrastructure system (disaster prevention / mitigation)
- ● To contribute to the community by utilizing big data including information directly obtained from the citizens, research center for disaster countermeasures is established
There are growing concerns among citizens over the recent intensifying natural disasters that have caused tremendous damage to the aging facilities and infrastructure. As a disaster countermeasure research base, we are working to build a framework to connect civic groups with the university and thus support the community by delivering academic information to the civilian world.
Research staff
Director / Professor
Dr. Eng.
Natural disaster science, Geotechnical engineering, Social system engineering / safety systems

Professor
Dr. Eng.
Geotechnical engineering

Research Assistant Professor
Dr. Eng.
Geotechnical engineering, Natural disaster science

Engineer
Geotechnical engineering

Associate professor
Dr. Eng.
Construction management, Disaster management, Administrative management

Professor
Dr. Eng.
Bridge engineering, Steel structures

Professor
Dr. Env.
Spatial information science, Urban / transportation planning, Urban geography

Professor
Dr. Env.
applied mechanics,data analysis

Associate Professor
PhD (in Natural Science specialising in Physical Geography)
Urban meteorology, Severe weather

Lecturer
Dr. Eng.
Coastal Engineering

extramural cooperation
Koichi Nagao

extramural cooperation
Dr. Eng.
Takamitsu Sasaki

Research Introduction
Research on disaster prevention and mitigation measures against natural disasters such as earthquakes and heavy rains
To mitigate the threat of natural hazards such as earthquakes and heavy rains, with an emphasis on geotechnical disasters such as liquefaction, landslides, or flood disasters, we are exploring new solutions through our unique research facilities followed by returning the obtained knowledge to the society. Some of our completed and ongoing research projects are described below.
Floods
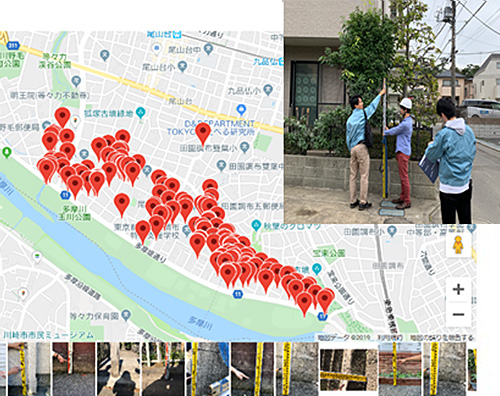
Survey and analysis of flood disaster caused by the East Japan typhoon in 2019
Landslides

Geotechnical centrifuge modelling to investigate the slope failure due to the debris flow
Earthquakes
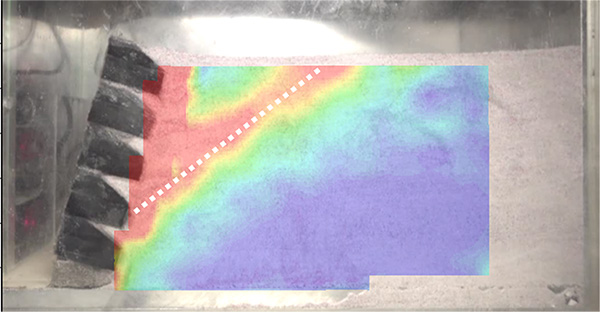
Geotechnical centrifuge modelling to study the collapse of retaining wall during an earthquake
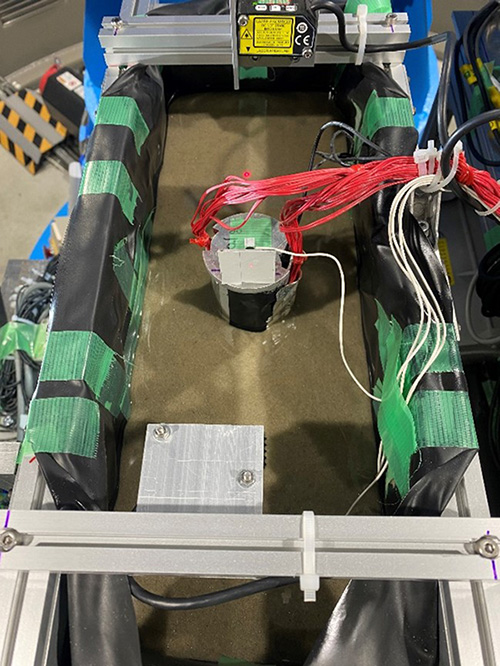

Geotechnical centrifuge modelling to investigate the behavior of monopile foundation for an offshore wind turbine in liquefiable soil
Development of risk index for natural disasters and its application
There are several natural disasters that a land can suffer from, although there are regional differences in the catastrophic and economic impact caused by them. It is thus necessary to develop natural disaster risk indicators that could cover all the natural disasters. This study examines the development of natural disaster risk indicators and their application to soft and hard measures of natural disasters.
Natural disaster risk index GNS
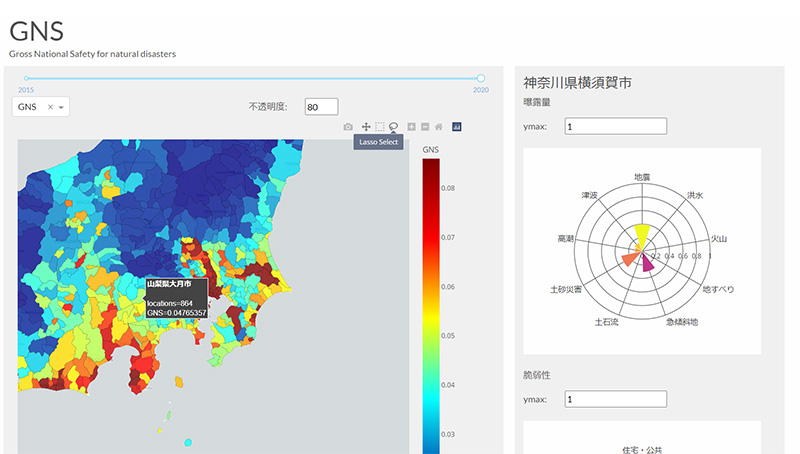
Development of an estimation technique for economic damage assessment considering local economic potential in the event of flooding
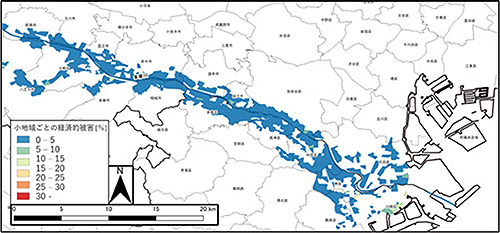
Tama river basin
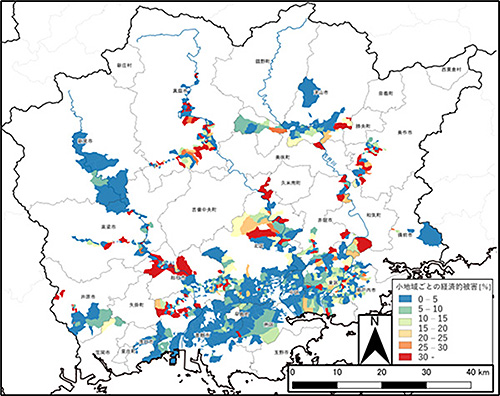
All of Okayama prefecture
Research on labor environment and disaster mitigation in construction projects
To conduct research on the improvement of labor environment at the construction projects, including from the perspective of preventing industrial accidents. Specifically, we will study risk management for the municipal organizations and reconstruction after the natural disasters.
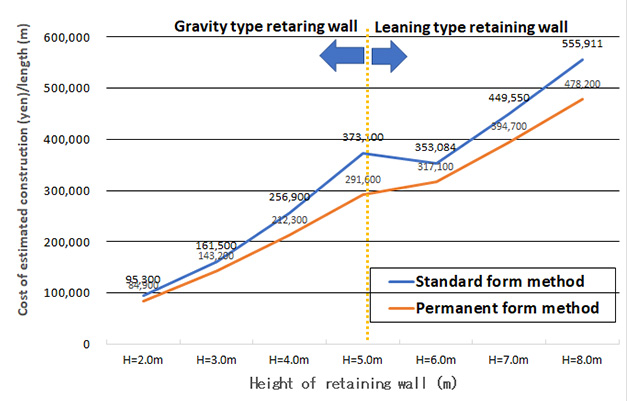
Comparison of construction cost between the general framework and permanent form of construction method for the retaining wall
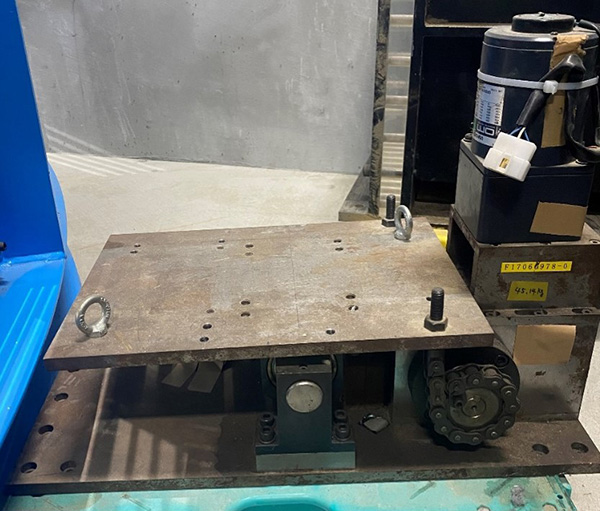
Distinctive Devices
Geotechnical Centrifuge
The Mark III geotechnical centrifuge device at the Tokyo City University (TCU) has a 10 G-ton capacity and can reach a maximum centrifugal acceleration of 100 G with an effective radius of 1.4 m. The newly developed medium-size centrifuge apparatus will provide the researchers at the TCU a cutting-edge technology to perform various geotechnical and soil-structure-interaction related experiments, and which will be used to further validate the numerical models. Furthermore, the researchers at the geotechnical centrifuge center of TCU have access to the mechanical cylindrical cam shaking table device, which is a novel shaker working on the mechanism of cylindrical cam. This allows the researchers to conduct research on geotechnical earthquake engineering, including assessing the impact of seismic loading on structural systems or proposing novel seismic mitigation techniques. Some of the equipment available at the geotechnical centrifuge center includes the mechanical jack to perform bearing capacity related research, a rainfall simulator to study rainfall-induced slope failure mechanism and a centrifugal tilting table to apply pseudo seismic loading. Prior to the installation of the new geotechnical centrifuge device in 2022, TCU was home to the smaller size centrifuges (Mark I and Mark II centrifuge) which had an effective radius of 0.5m and 0.4m respectively and were used for education and research for over 25 years. Some of the instrumentations available to measure soil-structure system response includes the pore pressure transducers, accelerometers, displacement sensors, strain gauges and laser displacement sensors.
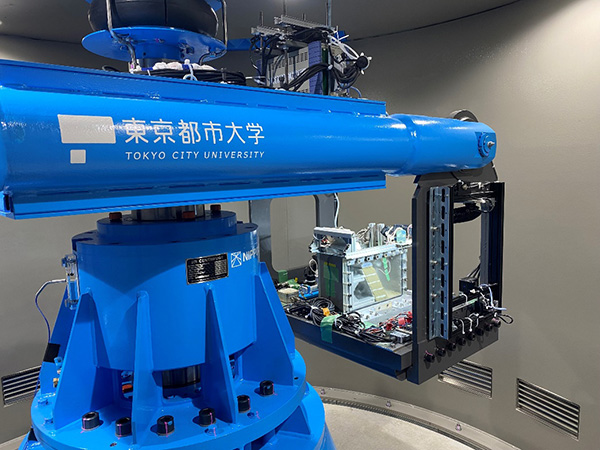
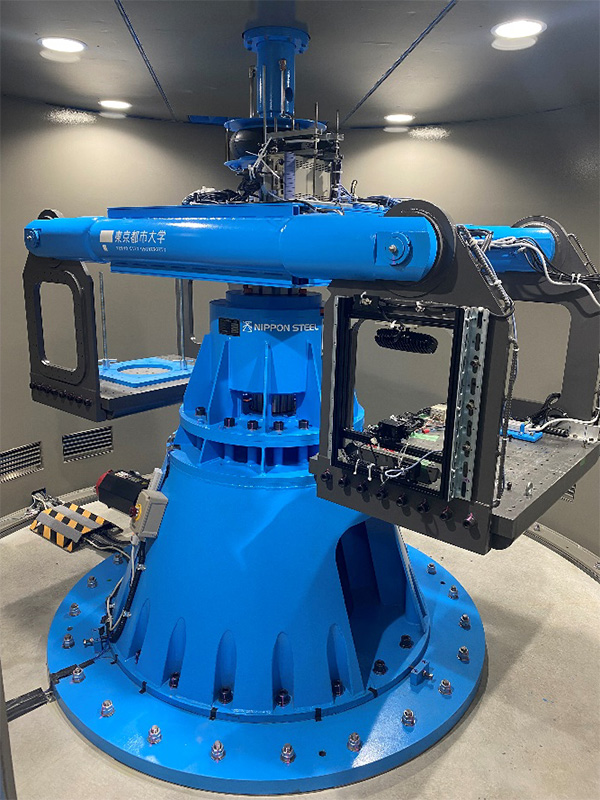

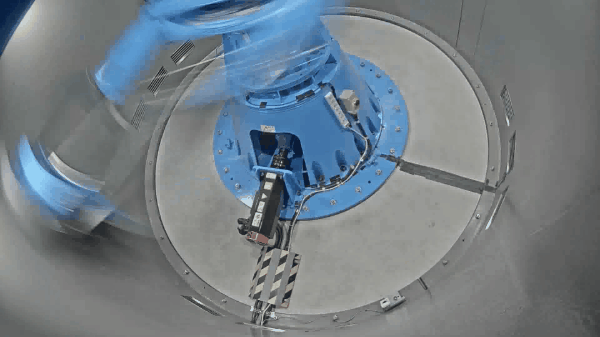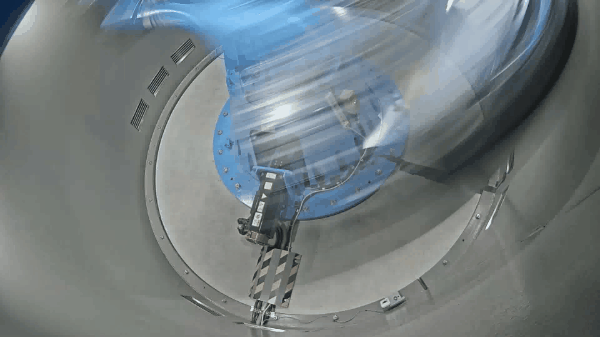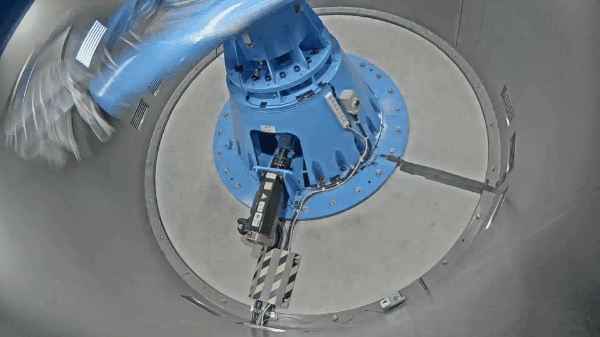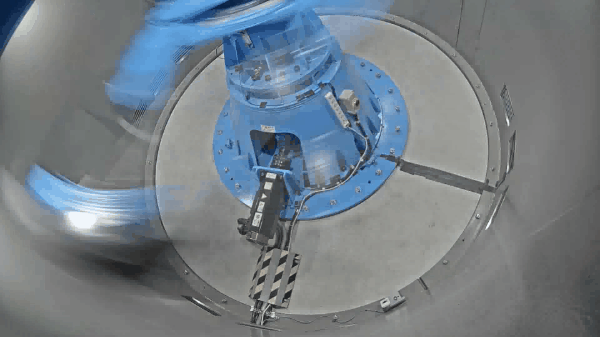

The specifications of the mark III geotechnical centrifuge device are described below.
| Max. centrifugal acceleration | 100G |
|---|---|
| Radius to base of platform | 1.4m | Max. rotation speed | 252.8rpm | Max. payload | 500kg | Capacity | 10G・ton | Motor capacity | 14kW | Beckett area | 0.6m×0.8m |
Some of the major equipment available at the geotechnical centrifuge center are described below
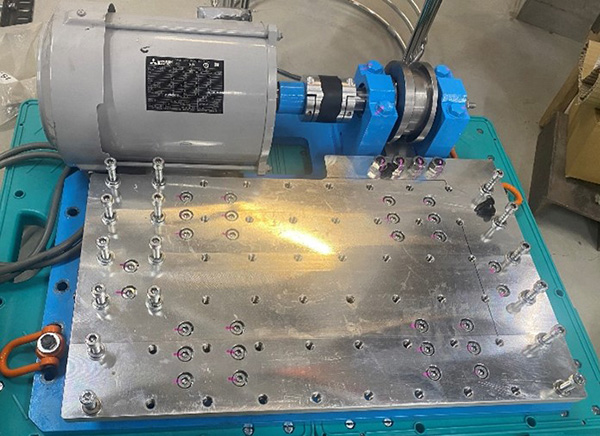
1.Mechanical Shaking Table
A shaking table apparatus driven by a mechanical hollow cam was developed in 2023 to conduct earthquake related research.

2.Rainfall simulator
This device is primarily used to conduct research on understanding the failure mechanism of geotechnical structures subjected to rainfall.
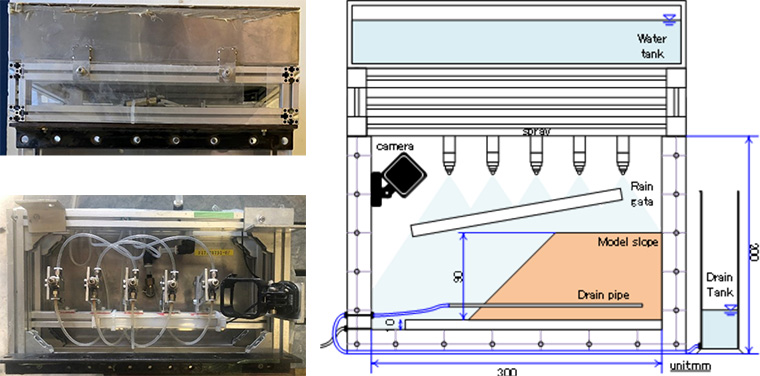
3.Tilting table test apparatus
The pin-coupled tilting table can be tilted to a maximum of 30 degrees at a speed of about 0.16 degree/sec and can apply a horizontal seismic force kh=tanθ (kh=horizontal seismic force, θ=tilting angle) on the structures. This device is primarily used to conduct research on the retaining wall systems.


